Lasciate che Istar vi aiuti a iniziare il vostro progetto con la nostra esperienza e il nostro know-how!
Caricate i file del vostro progetto e i requisiti di produzione e vi risponderemo entro 30 minuti!

What is the difference when you look at alloy and carbon steel? That’s a very good question. Picking the right kind of steel can make a project succeed or fail. If you have ever wondered about this, then this article is for you. I am going to explain the differences between alloy and carbon in a simple way. You will learn what makes each type of steel special. You will also learn where each one is used and how to choose the right one for what you need. It is not as hard as you might think!
At its heart, steel is a metal alloy. What does that mean? It means it is a mixture of metals. The main part of every steel is iron. But iron by itself is not always strong enough for the jobs we need to do. Because of this, we add other things to it. The most important added thing is carbon.
So, every type of steel you see is a mix of iron and carbon. The amount of carbon, and any other materials mixed in, is what makes all the different steel types we use. You can think of it like baking a cake. Iron is like your flour. Carbon is like your sugar. You must have flour and sugar to make a cake. In the same way, you must have iron and carbon to make steel. This simple mix is the starting point for everything else we will discuss.
Now, let’s talk about the most common kind of steel: carbon steel. I sometimes call it the “regular” version in the world of steel, but do not let that make you think it is weak. It is very, very useful. Carbon steel consists almost completely of iron and carbon. The rules say that for a steel to be called “carbon steel,” it should not have more than 2% carbon. It also has very tiny amounts of other materials that are not measured.
The important thing to remember is that carbon steel contains no large amounts of other alloying elements. Its features, like hardness and strength, depend almost completely on the amount of carbon inside. A little more carbon can make the steel much harder. A little less carbon makes it softer and easier to bend. This is why carbon steel can be used in so many different ways. We can change how it acts just by changing the carbon content. It’s a simple, good, and often low-cost steel for a very large number of jobs.
When we talk about carbon steel, we often put it into three groups. I have used all three for different projects. It’s important to know the difference. The groups are based on the carbon content.
Now we can talk about the next part: alloy steels. If carbon steel is the regular kind, then alloy steels are all the special types. To make alloy steel, we start with carbon steel. Then, we mix in other materials on purpose. These are called alloying elements. They are put in to give the steel special features that plain carbon steel does not have.
An alloy steel contains exact amounts of materials like manganese, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium. And there are many more! Each of these additional elements changes the steel in a special way. For instance, adding chromium can help the steel stop rust. Adding molybdenum can help it stay strong in very hot places. Alloy steel is mixed with these elements to make a material that is perfect for a certain, hard job. It is all about making the steel just right for the work it needs to do. This is how we get super-strong alloy steel for the aerospace field or tough tool steel for a factory machine.
The science behind this is very interesting to me. Just a small bit of an alloying element can totally change how a steel acts. These materials change the steel from the inside. They change its structure. Let’s look at a few of my favorites and see what they do.
Chromium is a very important one. When you add enough chromium (usually more than 10.5%), you make a well-known type of alloy steel called stainless steel. The chromium makes a very thin layer on the top of the steel that you cannot see. This layer keeps air and water away from the steel, which stops rust. This gives it great corrosion resistance. Nickel is another good one. It makes steel tougher. It also makes it stronger in very hot and very cold temperatures. When you mix chromium and nickel together, you get some of the best stainless steels.
Then there are materials like molybdenum and vanadium. Molybdenum helps the steel keep its high-temperature strength. This is very important for things like jet engines or parts inside a power plant. Vanadium is very good for steel. A little bit makes it much stronger and adds to its hardness and wear resistance. By mixing these alloying elements in different ways, we can make a long list of alloy steels. Each one has its own special properties of alloy steel for thousands of different steel applications.
This is a big question that people ask me. Most of the time, the answer is yes, alloy steel stronger. But it is a little more complicated than that. The strength of alloy steel is because of those added alloying elements. They help make a stronger structure on the inside of the steel. This makes it harder for the material to break or bend when you put pressure on it. This means alloy steels usually have a higher tensile strength when compared to carbon steels.
High-alloy steel, which has large amounts of alloying elements, can have a superior strength. It is much stronger than what even high-carbon steel can be. This is why we use alloy steels for the hardest jobs. These jobs include making armor, parts for high-pressure systems, or landing gear for airplanes. The overall strength of these special steels is incredible. But, a high carbon steel can be harder than some low-alloy steel kinds. So, “stronger” can mean different things. But if you compare them directly for pure high strength, an alloy steel is almost always the winner.
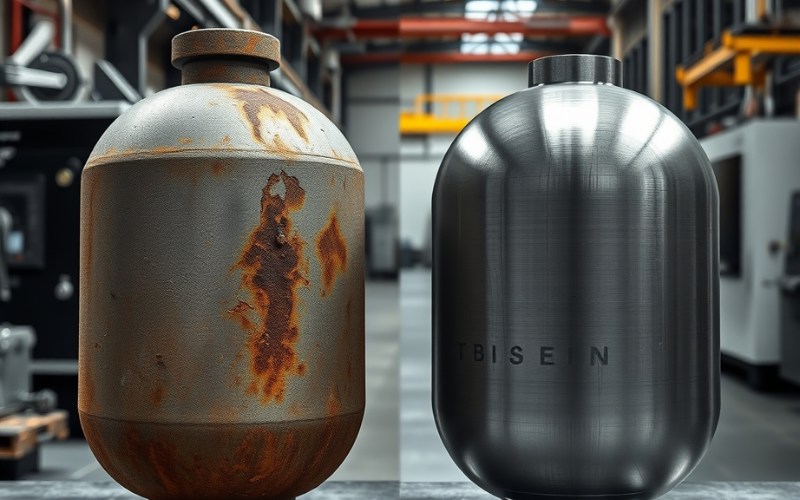
When you talk about stopping rust, one is much better than the other in the alloy steel vs carbon steel comparison. Carbon steel is not good at stopping rust. It is mostly made up of iron and carbon, so it rusts easily when it is around water. We often need to paint it, put a coating on it, or galvanize it to keep it safe. I have had to work with rusty carbon steel parts many times. It is always a challenge to protect them from the weather.
This is where alloy steels are much better, especially stainless steel. Like I said before, the chromium in stainless steel makes a protective shield. This gives it fantastic corrosion resistance. That is why we use stainless steel for kitchen sinks, tools for doctors, and equipment in the chemical processing sector. These are places where the steel needs to stay clean and not get rusty. Not all alloy steels are stainless. But many are made to have better corrosion resistance and strength. This makes them a smarter pick than carbon steel in wet places or areas that cause rust.
The best way to see how alloy and carbon steel are different is to look at where we use them. I have seen people use both kinds of steel in almost every industry you can think of. They are often used for different jobs because of their different features.
Here is a simple table that shows some common uses:
| Type of Steel | Caratteristiche | Usi comuni |
|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Soft, easy to form, welds well | Car bodies, pipes, building frames, signs |
| Medium Carbon Steel | Good mix of strength and ability to bend | Gears, axles, train tracks, machine parts |
| High Carbon Steel | Very hard, does not wear down easily | Knives, drill bits, springs, cutting tools |
| Alloy Steels | High strength, hardness, stops rust, and more | Jet engines, building machines, tool steel, car parts |
You can see that the applications of carbon steel are very common. It is the steel used for most common jobs and everyday things. Alloy steels, on the other hand, are for special jobs. They are used when the situation is very tough. In the automotive sector, you can find carbon steel in the body of a car. But you will find high-strength alloy steel in the engine and other important parts. Both carbon and alloy steel are very important to the world we live in.
If you are making a machine or a part, you have to decide. So, what’s the difference when you are picking one? I always tell people to think about three main points: what it needs to do, where it will be, and how much it costs.
First, what does the part need to do? If it needs to be very hard to cut something, you might choose a high carbon steel. Or you could choose a special tool steel, which is a kind of alloy steel. If it needs amazing yield and tensile strength to hold heavy things, like in the aerospace industry, then a high-alloy steel is the only option. If it is just a simple part that holds something in place, a low carbon steel is likely good enough.
Second, what kind of place will the part be in? If it will be outside or in a wet area, the corrosion resistance of an alloy steel like stainless is a big help. For a dry, indoor machine, carbon steel is often just fine. Third, how much money can you spend? Carbon steel is nearly always cheaper than alloy steel. The alloying elements that are used to make alloy steels cost a lot of money. You do not want to pay for the special features of an alloy steel if you do not need them. The best steel is the one that gets the job done safely for the lowest price.

So, after learning all this, what is the main point to remember in the alloy steel vs carbon steel talk? I hope you can see it is not that one is better than the other one. They are just different from each other. They are two different tools that you can use for two different types of jobs. The alloy vs carbon steel differences are because of what’s inside them.
Carbon steel is simple. What it can do is decided by its carbon content. It is a strong, good, and low-cost steel that we use for so many things. Alloy steel is more complicated. Alloy steel incorporates other materials to give it special abilities. These include amazing strength, wear resistance, or the power to stop rust. It is a steel that can do very difficult jobs that carbon steel is not able to do. The main differences between alloy steel and carbon steel show us their roles in the wide range of industries where steel is useful.
Let me give you a few key ideas. I always think a short list helps me remember the important things.