Tecrübemiz ve bilgi birikimimizle Istar'ın projenize başlamanıza yardımcı olmasına izin verin!
Tasarım dosyalarınızı ve üretim gereksinimlerinizi yükleyin ve 30 dakika içinde size geri dönelim!
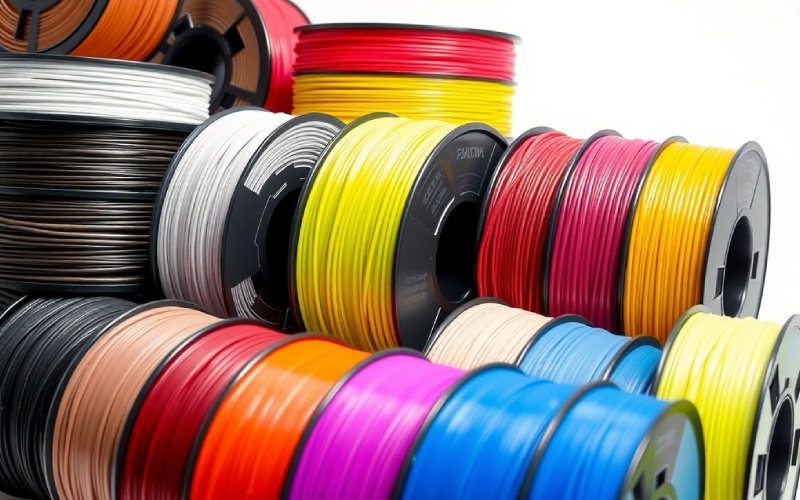

This article is your guide to learning about the different kinds of 3D printer filaments. I will share what I have learned to help you choose the best material for what you need. This will make sure the things you create are strong, look good, and work well. It does not matter if you are new to this or have a lot of experience. You will find helpful information here.
This guide will show you the most popular 3D printer filaments. We will start with the easy-to-use PLA and go to the strong ABS and the useful PETG. We will look at special filaments, like ones filled with wood or metal. We will also talk about strong materials used for factory work. When you finish reading this article, you will know exactly which filament type is best for your 3D printing projects.
In my time working with 3D printers, I have learned that the filament is like the ink for a normal printer. It is the material that turns your computer designs into real objects. 3D printer filaments are long, thin strings of a plastic material called a thermoplastic. This string is wound around a spool. You load this spool into the 3D printer. The filament is then pushed through a hot nozzle, which is called an extruder. The extruder melts the thermoplastic. It then puts down the melted plastic layer by layer to make your 3D printed object. This method is called Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication.
There are many kinds of 3D printer filaments you can buy. Each one has its own special features and uses. The thickness of the filament is a very important thing to check. The two common sizes are 1.75mm and 2.85mm. It is very important to use the right size for your 3D printer. This helps make sure the printing process goes smoothly and turns out well. The filament type you choose will decide the features of your final printed parts. This includes how strong they are, if they can bend, and how well they resist heat.
The number of 3D printing filaments has grown a lot from the few choices in the past. Today, you can find a huge number of materials. These go from common plastics like PLA and ABS to special composite filaments. These special filaments mix in materials like carbon fiber or wood. This large selection lets you make objects with specific mechanical properties for different jobs. Knowing about the properties of different filaments is very important to get the best results from your 3D printers.
Picking the right filament is a very important step. I always tell people to think carefully about this for any 3D printing project. The filament you pick has a direct effect on the quality, strength, and life of your 3D printed parts. To pick the best one, you need to think about what your project needs. For example, if you are making a part that needs to work and be strong, you might pick a material like ABS or PETG. But, if you are making things for decoration or first-draft models, the ease of printing with a filament like PLA might be more important.
Another important part of filament selection is what your 3D printer can do. Different 3D printers have different limits. For instance, some materials need higher print temperatures that not all extruders can get to. Filaments like ABS and Nylon often need a heated print bed. This helps stop them from bending during the printing process. You should also think about if your 3d printer has a cover. A cover is often needed for printing with materials that are affected by changes in temperature.
Lastly, think about where your 3D printed object will be used. Will it be in the sun, in the heat, or around chemicals? Some filaments are better at resisting sunlight or chemicals than others. For things that will be used outside, a material like ASA is a good choice because it holds up well in the weather. This would be a better choice than PLA, which can get weak in the sun. By thinking about all these things, you can make a good choice and pick the best filament type for your needs in 3D printing.
In my work, I have found that a few common 3D printer filaments are good for a lot of different uses. For anyone who is new to the world of 3D printing, Polylactic Acid (PLA) is almost always the best one to start with. It is a thermoplastic that can break down naturally. It is made from things we can grow, like cornstarch. This makes it a good choice for the environment. PLA is famous for being easy to print with. It has a low printing temperature and does not bend much. It also does not need a heated bed. This makes it the top choice for new users and for making detailed models that are for looks.
Another very popular filament is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). This thermoplastic is known for being strong, tough, and good at resisting heat. I have used ABS to make parts that need to work and handle higher temperatures and physical force, like gears or parts that fit together. But, printing with ABS can be harder than printing with PLA. It needs higher print temperatures for both the extruder and the print bed. This is to stop the printed parts from bending. It also lets off fumes during printing, so you need to be in a place with good airflow.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) is a filament that I think has a good mix of the features of both PLA and ABS. It is stronger and can bend more than PLA. It is also easier to print with than ABS. PETG is known for being strong, hard to break, and resistant to chemicals. This makes it a good pick for machine parts and covers. It also has the benefit of being safe for food, but you should always read the maker’s instructions first.
Here is a quick comparison chart of these popular filaments:
| Filament | Güç | Ability to Bend | Toughness | How Easy to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Orta | Düşük | Orta | Kolay |
| ABS | Yüksek | Orta | Yüksek | Orta |
| PETG | Yüksek | Orta | Yüksek | Orta |
When I was new to 3D printers, learning the difference between PLA and ABS was a big help. These are two of the most used 3D printer filaments, but they have very different features. Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a type of plastic made from plants. This makes it a better choice for the environment. It is the number one filament for beginners because it is very easy to use. PLA has a lower melting temperature and does not bend as much as ABS. This means you often do not need a heated print bed. But, PLA can break more easily and is not as good with heat as ABS is.
On the other hand, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic made from oil. It is known for being tough and hard to break. I often use ABS for 3D printed parts that need to be strong and handle higher temperatures. You can think of it as the same material used for LEGO bricks. The printing process with ABS is harder. It needs higher print temperatures and a heated bed. This is to stop the material from getting smaller and bending as it gets cool. It also creates fumes during printing, so having fresh air is very important.
Deciding between PLA and ABS really depends on what your 3D printing projects need. If you are making detailed models, first drafts, or things that will not be under a lot of force, PLA is a great and easy choice. If you need to make strong, tough parts that can take some heat and force, then ABS is the better choice. Just be ready for a printing process that is a little harder.
Yes, and they create many new and exciting options for your 3D printing projects! I have really enjoyed trying out flexible filaments. These materials are often called Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) or Thermoplastic Polyurethanes (TPU). They let you make 3D printed parts that are soft, can stretch, and feel like rubber. You can think of things like phone cases, things you can wear, and custom seals. The power to make flexible materials with 3D printers is a wonderful part of this technology.
Printing with flexible filaments can be a little hard, especially for new users. Because the material is very soft, it can sometimes get stuck in the extruder. I have learned that printing at a much slower speed is very important for good results with these materials. It is also important to have the correct type of extruder. A direct drive extruder is usually suggested over a Bowden extruder because it gives you better control over the flexible filament. Even with the difficulties, the final products are worth the work. They give you printed parts with special features.
There are different amounts of flexibility you can get. This means you can pick a filament type that is just right for your project’s needs. TPU is a popular kind of TPE. It is known for being a bit easier to print with but still very stretchy and hard to wear down. These flexible materials are tough and very resistant to impact. This makes them good for a lot of working uses where you need both strength and the ability to bend.
Of course! For me, this is where 3D printing technology becomes really fun. Composite filaments are a kind of 3D printing filament that mixes a main thermoplastic, like PLA, ABS, or Nylon, with tiny pieces of other materials. This makes a new filament with better features. Carbon fiber filaments are a well-known example. By putting small carbon fibers into a main material, you get a filament that is much stronger and more rigid. This gives the filament better shape stability and makes it less likely to bend.
I have used carbon fiber filaments to make 3D printed parts that are light but very strong. These are great for uses in flying machines, cars, or for making powerful drone parts. The finished printed parts often have a special non-shiny look that appears very professional. In addition to carbon fiber, there are other kinds of composite filaments you can get. Wood-filled filaments have tiny wood pieces in them. This gives your prints the look and feel of wood. You can even sand them and put a finish on them! There are also metal-filled filaments that have fine metal dust in them. This makes the printed parts heavier and gives them the look of metal.
One key thing to keep in mind when using these composite filaments is that they can cause wear. The hard pieces in them can wear out a normal brass nozzle on your 3D printer very fast. I found this out myself. You will need to use a nozzle made of hardened steel or another material that resists wear. This will stop you from having to change nozzles often and will make sure your printing process is steady. These filaments can cost a bit more, but the special properties and applications they allow for can really improve your 3D printing projects.
Support filaments are a special kind of 3D printing filament that I think are very helpful, especially for difficult prints. When you have a 3D model with parts that hang over or have complex shapes, the 3D printer cannot just print on nothing. It needs something to build on top of. This is where support material is useful. Support filaments are used in 3D printers that have two extruders. One extruder prints the main object. The other extruder prints the support structures that you will remove later.
The best thing about support filaments is that they are made to be taken off easily after the printing process is done. There are two main kinds of support material. The first is a breakaway support. This is just a filament that does not stick well to the main material. This lets you break it off with your hands. The second kind is my favorite. It is a support material that can dissolve, like PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) or HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene).
PVA is a support filament that dissolves in water. After your print is done, you can just put the whole object in water. The PVA supports will melt away. This leaves you with a clean and exact final part. HIPS can be dissolved in a chemical called limonene. Using a support material that dissolves is perfect for making complex shapes on the inside or very fine details. In these cases, taking off supports by hand would be hard or even impossible. These support filaments are a big help in getting top-quality results on hard 3D printing projects.

From my many years using 3D printers, I can say that knowing about filament properties and print quality is very important for good printing. The mechanical properties of a filament, like how much it can be pulled and how well it takes a hit, will decide how long your 3D printed parts last. For instance, a filament that can be pulled hard will handle more force before it snaps. These features are very important when you are making parts that need to work.
The printing temperature is another very important thing. Each filament type has a best temperature range for printing. If the temperature is too low, the layers of the print might not stick together well. This will make the object weak. If it is too high, the filament can get too liquid, and you will lose details. Good temperature control is the secret to getting layers to stick well and having a smooth surface. The glass transition temperature is the point when the thermoplastic starts to get soft. This is an important feature to think about for parts that will be around heat.
Also, some filaments are hygroscopic. This means they like to take in water from the air. Nylon is a good example of a hygroscopic material. If a filament takes in water, it can create issues during the printing process. You might hear popping or hissing sounds from the extruder. It can also make the surface of your printed parts look bad. This is why keeping your filament in a dry place is so important. By looking closely at the properties of the filament, you can adjust your printing settings and get the best print quality you can.
Besides the popular filaments, the world of 3D printing has an interesting variety of special and factory-grade materials that I enjoy trying for bigger projects. These filaments have special features for certain uses. For example, there are filaments that glow in the dark for making fun and pretty items. There are also filaments that change color when the temperature changes. There are even filaments that can carry electricity. These can be used to print basic electronic paths.
For tougher factory jobs, there are strong engineering filaments. Polycarbonate (PC) is known for being very strong, hard to break, and having a high glass transition temperature. This makes it good for uses in high heat. But, it can be a hard material to print with. It often needs very high print temperatures and a covered printer to stop it from bending. Another strong choice is nylon filament. It is very hard to wear down and tough. This makes it perfect for making gears and other parts that move.
There are also advanced composite filaments that are more than just carbon fiber. You can find filaments filled with glass fibers or even Kevlar. These give amazing strength and toughness. Materials like PEEK and PEI are on the very high end. They offer great resistance to heat and chemicals for the toughest factory jobs. These filaments are often more costly and need special 3D printers. But, they make it possible to create very strong, final-use parts with 3D printing technology.
Storing your 3D printer filaments the right way is a subject I always talk about. It might not seem like a big deal, but it can greatly affect how well your prints turn out. Many kinds of 3D printer filaments are hygroscopic. As I said before, this means they easily take in water from the air. When a filament spool is left out, it can get full of water. This leads to many problems with printing.
When a wet filament gets hot in the extruder, the water becomes steam. This can make bubbles and holes in your print. This will give you a rough surface and weak printed parts. You might also hear a crackle or pop sound from the nozzle during the printing process. To stop these problems, it is very important to keep your filaments in a dry place. I suggest keeping them in containers that are sealed from the air with packets that absorb water.
For filaments that are very likely to take in water, like Nylon and Polycarbonate, you might want to use a filament dryer before printing. This is a machine that heats the spool of filament to a certain temperature to get rid of any water it has soaked up. By doing these easy things to store your 3D printer filaments the right way, you can have a smoother printing process and get great quality results from your 3D printers all the time.