Let Istar help you get started on your project with our experience and know-how!
Upload your design files and production requirements and we will get back to you within 30 minutes!

You see low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, in grocery store bags, capture bottles, and that stick movie you utilize to cover leftovers. Yet what is it, truly? Why should you care? In this short article, I’ll break down every little thing you require to understand about LDPE plastic . We will certainly consider how it’s made, how it’s different from its cousin, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) , and where this incredibly typical material matches our world. Recognizing this humble plastic helps you comprehend the items you buy and the options you make everyday.
Allow me tell you concerning a material that is all around you. It’s called low-density polyethylene ( LDPE ). It is a sort of thermoplastic , which suggests you can warm it up, mold and mildew it into a form, and then cool it down. If you do this again, it will certainly melt and can be shaped into something else. This special plastic was the very initial grade of polyethylene ever before made, discovered back in 1933. It is made from a simple gas called ethylene . The chemical formula for this plastic product is (C2H4) n, which is the same as its relative, high-density polyethylene ( HDPE ). The “n” just indicates that the fundamental molecule repeats over and over in a lengthy chain.
So, what makes LDPE unique? As its name recommends, it has a reduced density than other sort of polyethylene . This makes it very flexible and light-weight. When you see a plastic item with the number 4 inside a reusing sign, you’ve discovered LDPE . Due to the fact that it is a low-cost and tough material, it is extensively made use of for making day-to-day items. Think of points like the plastic bags you access the food store or the clear plastic film used to wrap food. That’s usually LDPE at work. It’s an easy, functional plastic that has actually ended up being a significant component of our lives.
Now, you could be questioning exactly how we get this beneficial plastic . The magic takes place via a procedure called polymerization . Envision you have a huge box of paperclips. Each paperclip is a solitary unit, which researchers call a monomer . For LDPE , that monomer is a gas called ethylene . The polymerization process resembles connecting all those paperclips together to create a long chain. This lengthy chain is the polymer , and in this instance, it’s polyethylene .
To make LDPE , manufacturing facilities utilize an approach called free extreme polymerization (or radical polymerization ). It’s a bit like starting a chain reaction. This process requires really high stress — sometimes approximately 3,000 times the typical atmospheric pressure– and heat to function. Inside a special container, the ethylene gas is warmed and pressurized. An initiator, like a tiny bit of oxygen, is included in start the response. This causes the ethylene molecules to link up, producing the long polymer chains of LDPE . When the LDPE is created , it is cooled down and formed right into little pellets. These pellets, a kind of material , can then be melted down later on for molding into all kind of items.

You have actually heard me state HDPE , or high-density polyethylene . So what’s the difference between LDPE and HDPE ? Although they are both made from the monomer ethylene, they have extremely various properties . The major distinction, as you can presume, is density. HDPE is much heavier and much more stiff, while LDPE is lighter and a lot more adaptable. Think of a flimsy plastic grocery store bag ( LDPE ) versus a tough milk jug ( HDPE ).
The factor for this distinction depends on their molecular structure . I’ll chat more concerning this next, but basically, HDPE has right, organized chains that are snugly loaded with each other. In contrast, LDPE has chains with great deals of branches, making them messy and spread out. This architectural difference results in different attributes. HDPE is stronger and much more resilient than LDPE and has a higher melting factor . On the other hand, the flexibility of LDPE is its biggest stamina. Picking the best sort of plastic depends totally on the job you need it to do. If you require stiffness and strength , you select HDPE . If you require flexibility, you select LDPE .
Below is a basic table to reveal the main distinctions in between HDPE and LDPE :.
| Feature | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Lower thickness (0.91-0.93 g/cm THREE ) | Greater thickness (up to 0.97 g/cm FOUR) |
| Framework | Very branched polymer chains | Direct polymer chains, even more crystalline |
| Flexibility | Extremely adaptable and soft | Rigid and tight |
| Tensile Toughness | Lower tensile toughness | Higher tensile toughness |
| Transparency | Commonly clear or clear | Opaque (not translucent) |
| Thawing Point | Lower melting factor (around 110 ° C) | Higher melting point (up to 130 ° C) |
| Common Uses | Plastic bags, films, press bottles | Milk containers, pipes, reducing boards |
| Recycling Code | # 4 | # 2 |
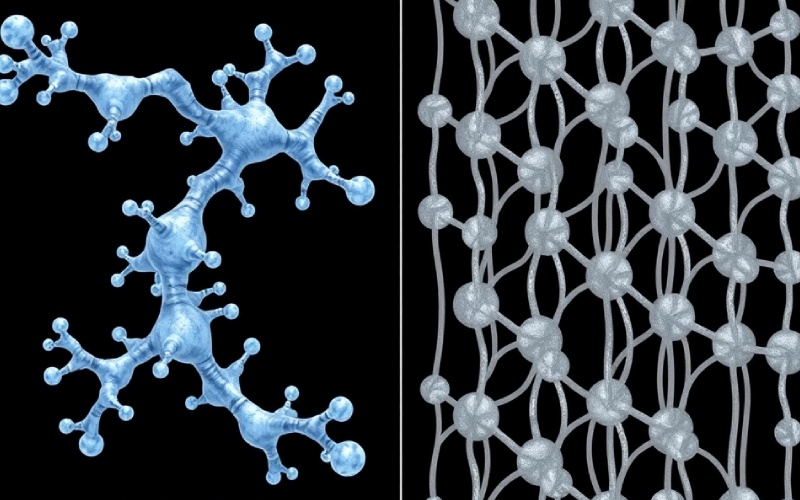
Allow’s obtain a little closer and check out the molecular structure of LDPE . This is where the genuine key to its residential properties lies. As I stated, polyethylene is a polymer , which is a gigantic molecule made of repeating systems. In this situation, the repeating units are ethylene particles, each with two carbon atoms . Throughout the polymerization of ethylene , these systems link up to form long chains.
The essential attribute of LDPE is its high degree of branching . Visualize a tree. It has a major trunk, but numerous branches expand out from it in all directions. The polymer chains in LDPE resemble that. These side branches avoid the chains from loading very closely with each other. This unpleasant, tangled setup of molecules is why LDPE has a lower thickness . Since the chains are not neatly straightened, the intermolecular pressures– the weak destinations between the molecules– are also weak. This is what offers LDPE its famous versatility and lower tensile strength . This structure is likewise much less crystalline , indicating it lacks the organized, repeating pattern discovered in even more stiff plastics like HDPE .
When I take a look at a product, I need to know its core functions. What makes it useful? The buildings of LDPE are what make it among the 2 most usual kinds of polyethylene . First and foremost is its adaptability. You can flex and stretch LDPE without it breaking quickly, which provides it great strength and high impact strength . This ductility is best for products that require to offer a little, like capture containers or the lid on your coffee.
An additional vital function is its chemical resistance . LDPE stands well against many acids and bases, which is why it’s made use of for containers in both homes and labs. It is additionally a good moisture obstacle, keeping water out of plans. Nevertheless, it does have a reasonably reduced melting point , so you can’t utilize it for things that get really warm. It additionally has a lower tensile strength compared to HDPE , implying it’s less complicated to rive. However, for the several applications where severe stamina isn’t required, the one-of-a-kind characteristics of LDPE make it an excellent and low-cost choice.
You most likely use LDPE every day without even thinking about it. Its most common application remains in LDPE product packaging . That slim plastic film you use as cling movie to cover a bowl of food is a traditional example of LDPE . Its flexibility and transparency make it perfect for this task. The usual usage remains in plastic bags , specifically the ones you get from the supermarket. These bags are light-weight, solid enough to lug your food, and economical to make, which shows off the very best top qualities of LDPE .
However it does not stop there. LDPE is used for lots of other points you see regularly. Squeezable bottles for points like honey or ketchup are commonly made from this versatile plastic . The waterproof lining inside paper milk containers and juice boxes is additionally made of LDPE . It is used for manufacturing different containers for the food and beverage market. You’ll also locate it in things like computer system components, research laboratory tools , and even toys. This type of polyethylene is absolutely a workhorse worldwide of durable goods.
Beyond our homes, LDPE is additionally a significant gamer in many commercial applications . Its one-of-a-kind combination of buildings makes it exceptionally versatile. As an example, due to the fact that it is so adaptable and has great chemical resistance , it is utilized to make tubing for bring liquids and chemicals. The electric market likes LDPE due to the fact that it’s a terrific insulator, so it’s typically utilized to cover wires and cables.
The material is also widely utilized in movie applications . Huge sheets of LDPE are utilized in building as vapor obstacles and in agriculture as greenhouse movies. Its influence resistance and strength indicate it can take care of challenging atmospheres without failing. Due to the fact that it is simple to collaborate with and has a low cost, markets can produce huge amounts of plastic parts efficiently. From shielding delicate electronic devices to aiding expand our food, LDPE is widely used throughout lots of fields, confirming its value far beyond the kitchen.
So, exactly how do we transform those tiny LDPE pellets I mentioned previously right into helpful items? The response is with molding . Because LDPE is a polycarbonate , it can be thawed and improved over and over. One of the most typical approach for forming LDPE is called injection molding . In this process, the LDPE resin pellets are warmed until they merge a liquid. This fluid plastic is then injected under high stress right into a mold, which is a hollow form in the shape of the final product, like a container lid or a container.
As soon as the mold and mildew is filled, it is cooled, and the LDPE strengthens into the wanted form. The mold and mildew opens, and the finished component is ejected. This molding process is very fast and effective, which is one reason LDPE products can be made so cheaply. Other procedures like blow molding (for containers) and extrusion (for movies and tubing ) are additionally utilized. The easy handling of LDPE is a huge advantage, enabling suppliers to create a substantial variety of plastic items with high precision. CNC machining is additionally feasible, though much less usual than with HDPE .
This is a huge concern in today’s world: can we recycle this plastic ? The response is of course, LDPE is a recyclable material. You can recognize it by the material identification code # 4. However, the ability to recycle it can be complicated. Stiff LDPE items, like a container or a lid , are typically less complicated to recycle through curbside programs. Several recycling facilities can refine these products without much problem.
The larger challenge comes with versatile LDPE items like plastic bags and plastic movie . These soft plastics can obtain entangled in recycling equipment, causing devices to jam and shut down. As a result of this, numerous towns and cities do not accept these items in their routine recycling containers. Instead, you can typically recycle them at special drop-off areas, like the collection containers you see at the front of lots of food store. When you recycle LDPE , it can be developed into brand-new products like trash can linings, flooring ceramic tiles, and even plastic lumber. So, while it takes an additional action, it deserves it to recycle your LDPE .
Besides this praise, you could believe LDPE is a perfect product. Yet like anything, it has its downsides. The largest negative aspect of making use of LDPE is possibly its fairly reduced stamina and rigidity compared to other plastics like HDPE . Its lower tensile strength indicates it can stretch and tear more conveniently under hefty tons. This is why you wouldn’t utilize it for something that needs to be very inflexible or hold a great deal of weight.
One more issue is that LDPE is extra vulnerable to something called stress and anxiety fracturing. This means that under specific problems, it can create little fractures over time, particularly when exposed to some chemicals. It also has a reduced thawing point , which restricts its use in applications that entail heat . And while LDPE is recyclable , the problems with reusing versatile movies suggest that too much of it still ends up in land fills. Identifying this drawback helps us make smarter selections concerning how and when we use this really typical plastic .
As we wrap up, here are the most crucial things I’ve found out about low-density polyethylene and intend to show to you: