Let Istar help you get started on your project with our experience and know-how!
Upload your design files and production requirements and we will get back to you within 30 minutes!

Not all 3D printing is the same. There are many different kinds of 3D printing. Each one has its own good points and bad points. It can be hard to understand. This article is here to help you. I will explain the most common 3D printing technologies in an easy way. You will learn how each 3D printing process works, what stuff they use, and what they are good at making. This guide will help you pick the best 3D print technology for your own projects.
Let me begin with the kind of 3D print technology that most people know about. It is called Fused Deposition Modeling, or FDM. I remember seeing my first FDM printer at a workshop. It was really cool to watch it build an object one layer at a time. An FDM printer works a lot like a hot glue gun does. It uses a long string of plastic which is called a filament. The printer heats up a tiny piece of the plastic filament. It heats it until it melts. Then, it squeezes the melted plastic out of a tiny tip.
The printer moves this tip around to draw the shape of one layer of the object. After that layer is finished, the plate it builds on moves down just a little bit. The printer then begins to draw the next layer right on top of the first one. This process is done again and again. This is one of the most common 3D printing methods. The FDM printer continues to add another layer. It does this until the whole 3D print is done. This is why you can often see thin lines on an FDM 3D print.
FDM printing is very popular. This is because the printers are not expensive and they are simple to use. The thermoplastic material, like the plastic filament, is also cheap. This makes it a great choice for making a simple prototype. It is also great for people who do it for fun. But, FDM parts are not always as strong or as detailed as parts made with other 3D printing technologies. They usually have a rougher feel on the outside. But for a fast and cheap 3D print, Fused Deposition Modeling is a great choice.
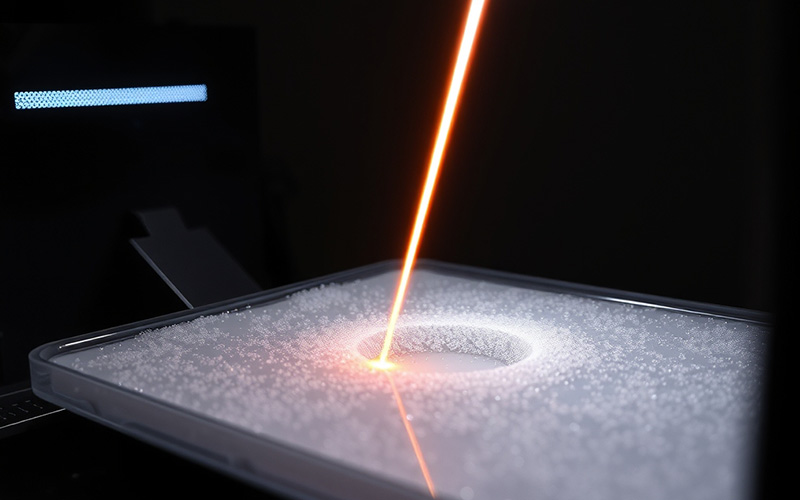
Now, we can talk about Stereolithography, or SLA. This was the very first of the 3D printing technologies to be invented. I think SLA is really cool because it can make things with tiny details. An SLA printer is not the same at all as an FDM printer. It does not use a plastic filament. Instead, it uses a liquid plastic. This liquid is called a photopolymer resin. The printer has a container of this liquid resin. It also has a build platform inside. An SLA printer uses a special ultraviolet (UV) laser to create the 3d print.
The 3D printing process for SLA is very exact. A UV laser beam is pointed into the container of resin. The laser carefully draws the first layer of the object. When the laser light hits the liquid resin, the liquid gets hard right away. This is called a cure. When the layer is done, the build platform moves up or down a little. The printer then gets ready to make the next layer. This SL process goes on until the 3D print is all done. This kind of 3d print needs support structures to hold up parts that stick out.
I often suggest SLA when a customer needs a prototype with a very smooth outside and very small details. The SLA parts look almost like they were made in a factory mold. The quality is really that good. The SL technology is great for making things like small statues, molds for jewelry, and models with a lot of detail. The resin and the SLA printer can cost more money. But the great look of the final 3D print is often worth the extra cost. This is a very common kind of 3d print. SL is a very useful tool. A lot of 3d print jobs use SLA.
Digital Light Processing, or DLP, is another kind of 3D printing that uses resin. It is a lot like SLA, but there is one big difference. I like to imagine DLP is a cousin to SLA. Both of them use a liquid photopolymer to make a 3D print. They both use light to cure the resin. But the way they use that light is what makes them different. An SLA printer uses a laser beam to draw each layer. A DLP printer uses another way.
A DLP printer uses a special screen. It is like a screen for a movie projector. This screen shines a picture of a whole layer at the same time. You can think of it like using a rubber stamp. It cures the whole layer of resin with just one flash of light. Because it makes the whole layer at once, DLP can often be faster than SLA. This is especially true for bigger, solid parts. The 3D printing process is faster. This is a big benefit of Digital Light Processing. The 3d print can be finished very quickly.
The quality of a DLP 3D print is very good. It has a great surface finish, which is a lot like SLA. These different 3D printing methods are both great for making things with lots of small details. People use Digital Light Processing for many of the same projects as SLA. For example, they use it to make a detailed prototype or models for dentists. The main choice between SL and DLP usually depends on speed and the exact printer model. Both are great 3D printing technologies. The final 3d print will be very good.
Let’s change from liquids to powders. This is where things get really interesting to me. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is one of the types of 3D printing that uses a powder. It is usually a kind of plastic like nylon. An SLS printer puts down a very thin layer of this powder over the build area. This is a great 3d print method.
Once the layer of powder is down, a strong laser starts to work. The laser beam moves over the powder. It heats up certain spots, based on the 3D CAD design. The laser heats the powder until it melts and sticks together. This is also called fusion. The printer then puts another layer of powder on top. The laser heats the next layer, making it stick to the layer below it. The 3d print is built up this way inside a container of nylon powder.
One of the best things about SLS is that it does not need support structures. The loose powder all around the object holds up the 3D print while it is being made. This allows you to make shapes that are hard to make. These shapes would be difficult to create with FDM or SLA. Since SLS parts are made from materials like nylon, they are very strong and tough. This makes SLS great for parts that actually work, parts that snap together, and prototypes that need to be tested. The 3d print is very strong.
Multi Jet Fusion, or MJF, is a new kind of 3D printing process that is like SLS. I was very excited when MJF technology was first made. It also builds parts from a container of nylon powder. But it does not use a laser to make the powder stick together. Instead, MJF uses a different and faster way. An MJF printer has a row of tiny sprayers, much like a 2D paper printer.
The printer puts down a thin layer of powder. Then, the sprayer head moves over it. It sprays a special liquid, called a fusing agent, on the areas of powder that will become the 3D print. It also sprays a detailing agent around the edges to make them sharp. After the liquids are sprayed, a special heating lamp moves over the powder. The fusing agent soaks up this heat. This melts the nylon powder and makes it stick together. The area with the detailing agent stays as a powder.
This MJF process is very quick. It can produce parts from nylon powder much faster than many other 3D printing options. The MJF parts are very strong and flexible. They also have a slightly better surface finish than SLS parts. I have seen MJF used for making final parts, not just a prototype. It is one of the powerful manufacturing technologies you can use for a 3d print. The 3d print is very tough.
Yes, you can definitely 3D print with metal! This is one of the most high-tech 3d printing technologies. One way to do this is with Direct Metal Laser Sintering, or DMLS. The DMLS process is a lot like SLS. But it uses a very tiny metal powder instead of plastic powder. This could be steel, aluminum, titanium, or other metal mixes. A DMLS printer is a very strong machine.
Just like in SLS, a DMLS printer puts down a thin layer of metal powder. A very strong laser then scans the layer. The laser is powerful enough to melt the tiny bits of metal so they stick together. After one layer is put down and stuck together, the machine puts down another layer of powder. The laser then sticks this new layer to the one below it. This continues until you have solid metal parts. This 3d print method is amazing.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering is used to make strong, light, and complex metal parts. I have seen it used for airplane parts, medical body parts, and for making special tools. The DMLS process allows engineers to create metal parts with difficult designs. These designs would be impossible to make with older ways of making things. The 3d print can be very complex. This 3d print technology can form plastic and metal parts.
Electron Beam Melting, or EBM, is another way to make a 3D print with metal. It is like DMLS because it also uses a powder and melts it together to build metal parts. But, instead of a laser, EBM uses a powerful electron beam. This is a very important difference. The whole process happens in a space with no air in it, at very hot temperatures.
The electron beam is much stronger than the laser used in DMLS. This power lets it melt the metal powder all the way. This creates very strong parts with great material qualities. The hot temperature in the build area helps stop the final 3D print from bending or cracking. This means the parts are less likely to have problems. Electron Beam Melting is often used with materials like titanium mixes.
EBM is a wonderful choice for making parts that need to be very strong and work well. It is often used in the airplane and medical fields. The parts made with this 3D printing process are very solid and strong. The melting of the metal powder is very thorough. The machines cost a lot of money. But the ability to make very strong, complex metal parts makes EBM one of the key types of 3D printing technologies for important jobs.
PolyJet is a special kind of 3d print technology. It works like a normal inkjet paper printer, but it builds in 3D. I find PolyJet really interesting. This is because it can print with different materials and colors in just one 3D print. A PolyJet printer has a print head with hundreds of very small sprayers. This head sprays out tiny drops of photopolymer resin onto a build platform.
As the printer lays down these drops of photopolymer, a UV light shines on them. This makes them hard right away, turning them from a liquid into a solid. This process is done over and over again, layer by layer, to build the 3D print. Because it can use different materials at the same time, a PolyJet printer can make a prototype that has both hard plastic parts and soft, bendy parts. It can even mix materials to create different levels of hardness or different shades of color.
PolyJet is another plastic 3d printing method that is known for making models that look very real. It makes an extremely smooth surface and has very high levels of detail. I have used it for creating beautiful models of body parts and microfluidics. The parts are sometimes not strong enough for real-world tests. But for a prototype that needs to look good, PolyJet is one of the best 3d printing technologies. PolyJet is another plastic 3d printing choice that is truly great to see.

Picking the right technology from the different types of 3D printing can seem tricky. I tell people to think about three things. What will the part be used for? What amount of detail do you need? And how much money can you spend? The chart below gives an easy comparison of some of the sorts of 3d printing we have talked about.
| Technology | Main Material | Best For | Key Good Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | Thermoplastic filament | Cheap first models, projects for fun | Low cost, simple to use, quick |
| SLA (Stereolithography) | Photopolymer resin | Models with lots of detail, jewelry, dental | Very smooth outside, high detail |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | Nylon powder | Parts that actually work, complex shapes | Strong parts, no extra supports needed |
| MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) | Nylon powder | Parts that work, making a small number of items | Fast, strong and tough parts |
| DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) | Metal powder | Strong metal parts, airplane parts, medical parts | Strong, complex metal parts |
| PolyJet | Photopolymer resin | Real-looking models with many materials & colors | Looks like the real thing, smooth outside |
If you are just getting started, an FDM printer is a great choice. If you need a beautiful prototype with a perfect surface, you should look at SLA or PolyJet. For strong plastic parts that need to work, SLS or MJF are the best choices. And for the hardest jobs, DMLS can create amazing metal parts. Each 3d printing process has its own use.
When I look at the different kinds of 3d printing technologies we have today, I am excited about what’s coming next. Things are changing very fast. Printers are getting faster. They are also getting cheaper and can use a wider range of materials. We are seeing new 3D printing methods that can mix the good points of different processes. Soon, we might have one printer that can make a 3D print with the speed of MJF, the detail of SLA, and the material choices of FDM.
The world of 3D printing is always changing. These technologies are not just for making a prototype anymore. People are using them to make final products. This is making things faster and for less money. From houses to food to medical parts, the 3D print is changing the way we make everything. Learning about these types of 3d printing is the first step. It helps you become part of this amazing future. I am excited to see what happens next.